The Application of Laser Technology in Industry
Laser technology has made significant advancements in the industrial sector since the mid-20th century. It has not only improved production efficiency but also expanded the possibilities within manufacturing. This article delves into the extensive applications of lasers in various industrial domains, ranging from materials processing to measurement, manufacturing, and communication.

1. Materials Processing
Laser technology has played a pivotal role in industrial materials processing, including:
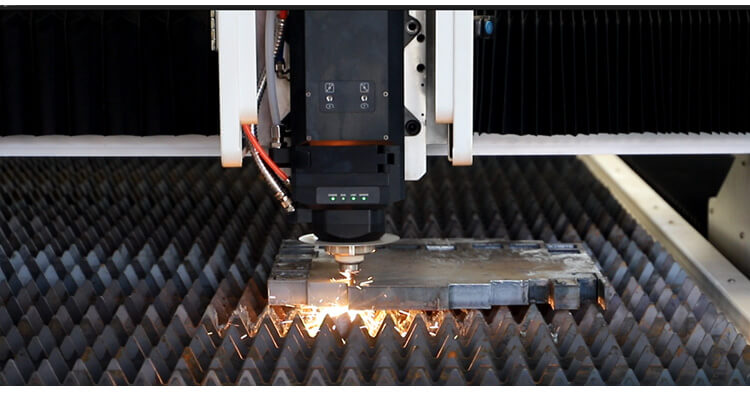
a. Cutting and Welding: Laser cutting finds widespread use in precisely cutting complex shapes in both metallic and non-metallic materials. It is employed in the fabrication of automotive components, aerospace parts, and electronic devices. Laser welding, on the other hand, allows the precise joining of metal components, often faster and cleaner than traditional welding methods.
b. Engraving and Marking: Laser engraving and marking technologies are used to create patterns, text, and logos on a variety of materials. This finds applications in jewelry making, sign manufacturing, and craftwork.
c. Surface Modification: Laser treatments enhance material surface properties. This includes improving the wear resistance of metals, enhancing plastic adhesion, or increasing the hardness of ceramics.
2. Manufacturing

a. 3D Printing: Laser-based 3D printing has gained prominence in manufacturing. It enables the layer-by-layer construction of complex 3D objects and is widely applied in prototyping, medical device production, aerospace, and automotive manufacturing.
b. Rapid Prototyping: Laser-based additive manufacturing allows for the creation of components with intricate internal structures, reducing weight while enhancing performance.
3. Inspection and Measurement
a. LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): LIDAR systems, utilizing lasers, are pivotal in measuring distances and mapping. They are integral in autonomous vehicles, robotic navigation, construction surveying, and environmental monitoring.
b. Non-Contact Measurement: Laser-based measurement technology accurately measures distances, dimensions, and shapes without physical contact, crucial for precise manufacturing and quality control.
4. Medical Applications

a. Laser Surgery: Laser technology is employed in medical surgeries such as laser vision correction, skin resurfacing, and dental procedures, offering precision and minimal invasiveness.
b. Medical Imaging: Lasers are utilized in medical imaging techniques like Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) for disease diagnosis and monitoring.
5. Communication
a. Fiber Optic Communication: Laser diodes are at the core of high-speed data transmission in fiber optic networks, ensuring faster and more reliable data transfer.
b. Laser Radar: Laser radar systems are used for high-speed data transmission and distance measurement, critical for advanced communication and navigation systems.
6. Cleaning and Cutting

a. Laser Cleaning: Laser technology is used for cleaning surfaces, including artworks, artifacts, and buildings. It removes adhered dirt and contaminants without damaging the underlying material.

b. Material Cutting: Laser cutting is employed in industries ranging from paper and textiles to leather and plastics, making it an essential tool in manufacturing and crafting.
In summary, laser technology has become an indispensable part of modern industry, driving innovation and progress across various sectors. As laser technology continues to evolve, we can anticipate exciting new applications that will provide further opportunities and challenges for industry.
















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.